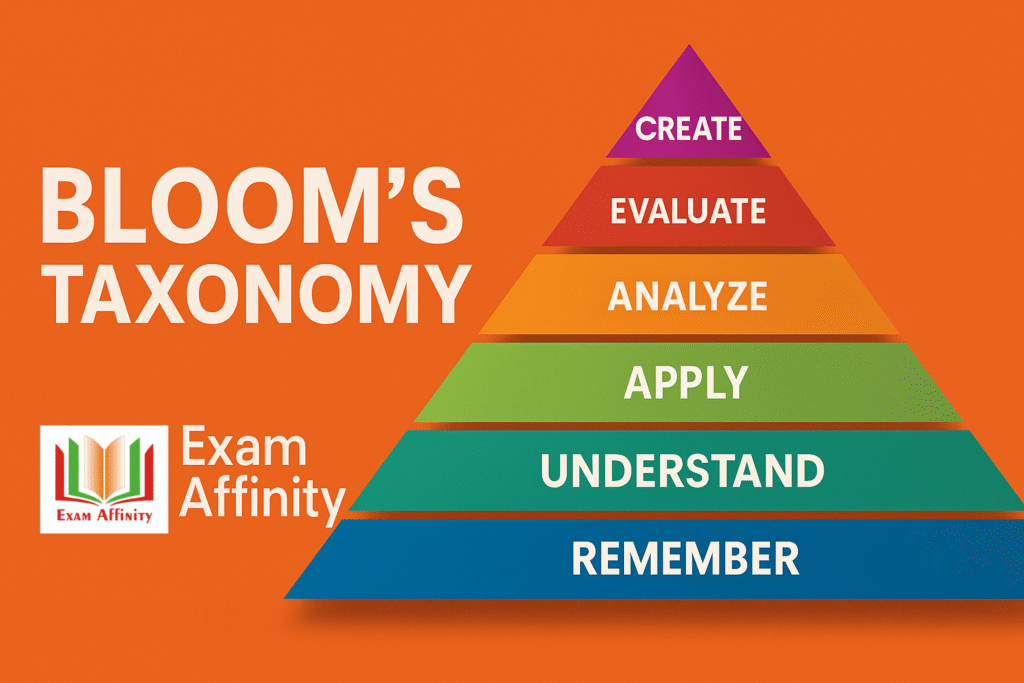
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a well-known framework used to classify educational goals. It organizes learning into three major domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Each domain addresses a different aspect of human learning, allowing educators to design balanced and meaningful learning experiences.
1. Cognitive Domain (संज्ञानात्मक पक्ष)
This domain deals with intellectual skills, thinking processes, and knowledge acquisition.
Originally introduced in 1956 and later revised in 2001, it shifted from noun-based categories to verb-based categories to highlight active learning.
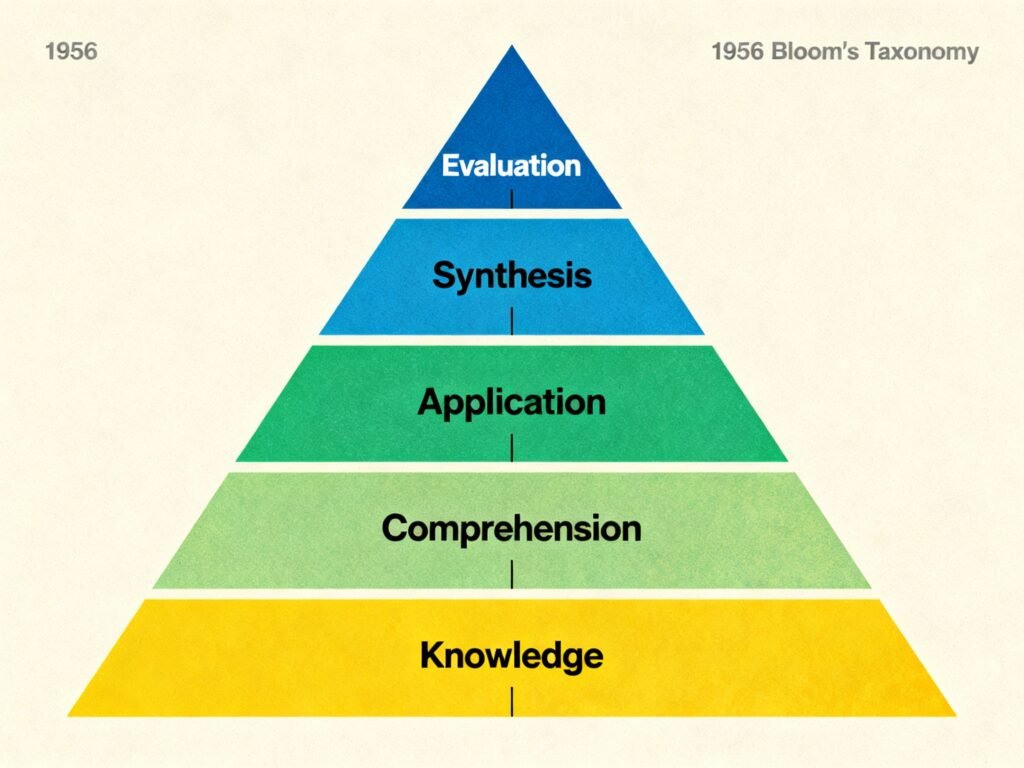
Original vs. Revised Cognitive Taxonomy
| Original (1956) | Revised (2001) | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | Remember | Recall facts or concepts | List the planets of the solar system |
| Comprehension | Understand | Explain ideas or concepts | Summarize a story |
| Application | Apply | Use knowledge in new situations | Solve a math problem |
| Analysis | Analyze | Break information into parts | Compare historical events |
| Synthesis | Create | Combine ideas into something new | Design a sustainable city |
| Evaluation | Evaluate | Justify decisions or ideas | Critique a scientific theory |
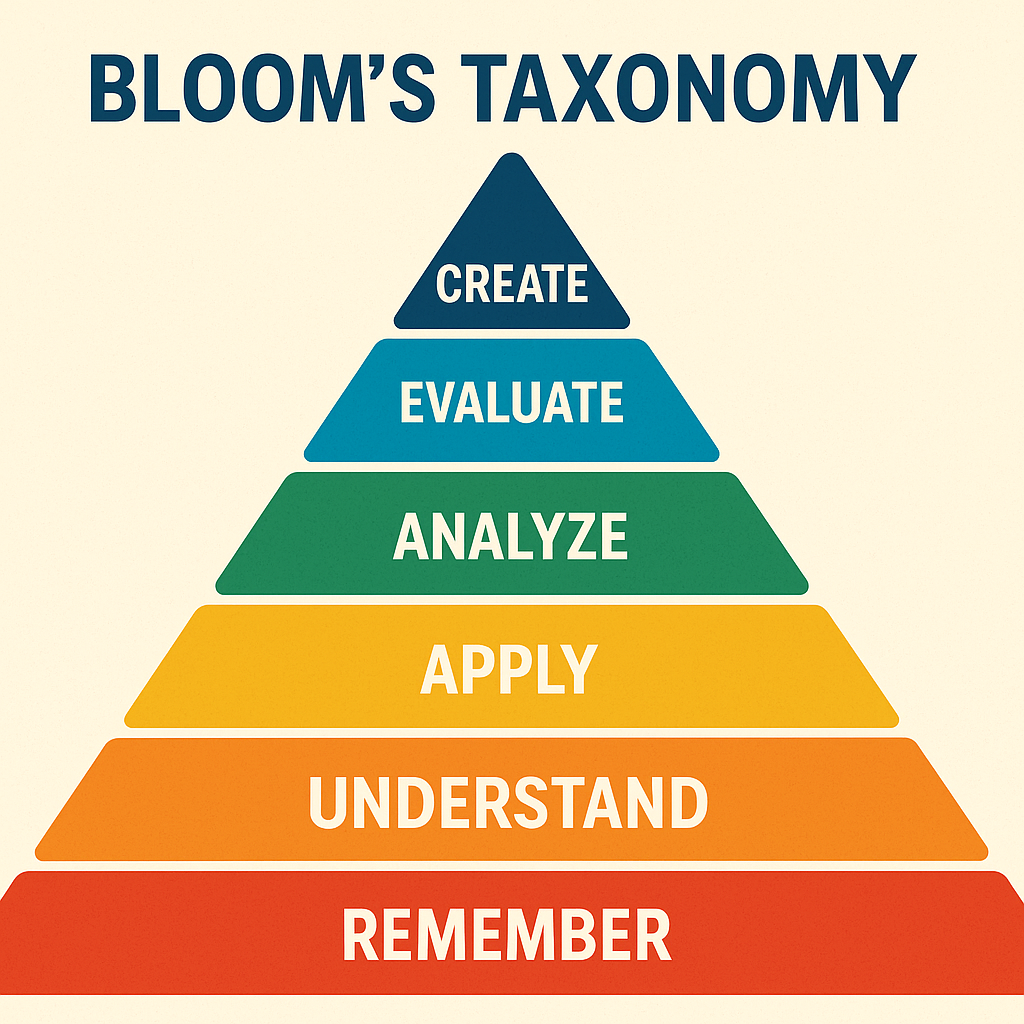
Through these levels, learners progress from recalling basic facts to producing original ideas.
2. Affective Domain (संवेगात्मक पक्ष)
The affective domain focuses on emotions, attitudes, values, and the development of a value system. Unlike the cognitive domain, which emphasizes thinking, this one emphasises feeling and meaningful internalization.
Levels of the Affective Domain
Receiving (Awareness)
The learner shows willingness to pay attention. For example, listening attentively during a lecture.
Responding (Participation)
Active engagement takes place. A learner might join a group discussion or answer questions.
Valuing (Attaching Worth)
The learner expresses attachment to a value. Advocating for environmental protection is one such example.
Organizing (Prioritizing Values)
Values are arranged into a system. A student may balance ethics and work responsibilities.
Characterizing (Internalizing Values)
The learner consistently behaves according to their values. Living sustainably shows this level of commitment.
3. Psychomotor Domain (गत्यात्मक पक्ष)
The psychomotor domain deals with physical skills, coordination, and motor movements. Although Bloom did not formally develop this domain, later scholars created a structured hierarchy.
Levels of the Psychomotor Domain
Imitation (Copying)
A learner copies an action shown by someone else, such as mimicking a dance step.
Manipulation (Performing)
Here, the learner performs actions independently, like assembling furniture.
Precision (Accuracy)
Tasks are executed with improved control and accuracy, such as painting fine details.
Articulation (Coordination)
Multiple skills are combined smoothly. Playing a piano piece illustrates this level.
Naturalization (Mastery)
The learner performs skills effortlessly. Expert-level yoga poses are a good example.

Glossary
| Term | Definition | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive | Mental processes used for knowledge acquisition | Cognitive |
| Affective | Emotions, values, and attitudes | Affective |
| Psychomotor | Physical skills and movement | Psychomotor |
| Analyze | Break down information to explore relationships | Cognitive |
| Evaluate | Make judgments using criteria | Cognitive |
| Valuing | Assign importance to an idea or belief | Affective |
| Naturalization | Mastering a physical skill effortlessly | Psychomotor |
Key Takeaways
Cognitive = Head (Thinking)
Affective = Heart (Feeling)
Psychomotor = Hand (Doing / Activity)
CTET Application-Based MCQs (Bloom’s Taxonomy + Pedagogy)
1. A teacher asks students to classify animals into groups based on their features. This activity belongs to which level of Bloom’s Taxonomy?
a) Apply
b) Analyze
c) Understand
d) Remember
2. A student is able to solve new maths problems by using previously learned formulas. This reflects—
a) Understand
b) Remember
c) Apply
d) Evaluate
3. A teacher asks students to justify whether a character in a story made a right or wrong decision. Which level is being targeted?
a) Analyze
b) Create
c) Understand
d) Evaluate
4. A child designs their own science project model after learning all concepts in the chapter. This is an example of—
a) Apply
b) Analyze
c) Understand
d) Create
5. A teacher asks students to summarize a poem in their own words. This requires students to—
a) Remember
b) Understand
c) Apply
d) Create
6. A student identifies the main idea and supporting details in a paragraph. This task reflects—
a) Remember
b) Create
c) Analyze
d) Evaluate
7. A teacher shows a model and asks students to replicate it step-by-step. This task falls under—
a) Analyze
b) Evaluate
c) Apply
d) Create
8. A teacher provides a new problem situation where students must use their reasoning and compare alternatives. This targets—
a) Remember
b) Understand
c) Evaluate
d) Apply
9. Students recall important dates and events of the freedom struggle. This activity is at which level of Bloom’s Taxonomy?
a) Analyze
b) Remember
c) Understand
d) Evaluate
10. A teacher asks students to design a new ending to a story. This is an example of—
a) Apply
b) Understand
c) Analyze
d) Create
Bloom’s Taxonomy – MCQs with Answers & Explanations
1. At the knowledge level, students will
(a) Argue the point
(b) Recall information
(c) Categorize topics
(d) Calculate distances
Correct Answer: (b) Recall information
Explanation:
The knowledge level of Bloom’s Taxonomy focuses on remembering and recalling previously learned facts, concepts, or information.
2. Which type of question is a sample of Evaluation?
(a) Do you agree with the actions of Sam?
(b) Why was it better than…?
(c) What sources can you use to support your opinion?
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation:
Evaluation involves making judgments, forming opinions, comparing ideas, and justifying decisions. All given options reflect evaluative thinking.
3. What you can invent or design is a sample of
(a) Knowledge
(b) Comprehension
(c) Application
(d) Synthesis
Correct Answer: (d) Synthesis
Explanation:
Synthesis involves combining ideas and elements to create something new, such as inventing or designing.
**4. “What questions would you ask Nelson Mandela in an interview?”
This question belongs to which level of Bloom’s Taxonomy?**
(a) Application
(b) Evaluation
(c) Analysis
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer: (a) Application
Explanation:
The learner applies knowledge about Nelson Mandela to frame meaningful interview questions, demonstrating application.
**5. “What ways could you change the plot of the story?”
This question represents**
(a) Synthesis
(b) Comprehension
(c) Knowledge
(d) Application
Correct Answer: (a) Synthesis
Explanation:
Changing the plot requires creative thinking and recombination of ideas, which is characteristic of synthesis.
**6. “Defend the actions of the main character.”
This question belongs to which level?**
(a) Evaluation
(b) Comprehension
(c) Analysis
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer: (a) Evaluation
Explanation:
Defending actions involves judging, justifying, and forming opinions, which are core features of evaluation.
7. Infer, follow, interpret, summarize, demonstrate, cite, and interpolate are verbs associated with
(a) Application
(b) Knowledge
(c) Synthesis
(d) Comprehension
Correct Answer: (d) Comprehension
Explanation:
These verbs indicate understanding, interpreting, and explaining information, which fall under comprehension.
8. If students construct a model to show how something works, they are
(a) Evaluating
(b) Applying
(c) Synthesizing
(d) Don’t know
Correct Answer: (b) Applying
Explanation:
Constructing a model requires learners to use their knowledge in a practical manner, which is application.
9. If a student prepares a visual presentation showing an updated version or new angle of a topic, he or she is
(a) Comprehending
(b) Applying
(c) Synthesizing
(d) Analyzing
Correct Answer: (c) Synthesizing
Explanation:
Presenting a new angle involves combining existing knowledge to create a new perspective, which is synthesis.
**10. Students first predict what will happen in a story, then list the main events, and finally write a review.
Which skills are being used?**
(a) Application, Synthesis, and Evaluation
(b) Comprehension, Knowledge, and Analysis
(c) Comprehension, Knowledge, and Evaluation
(d) Evaluation, Knowledge, and Synthesis
Correct Answer: (c) Comprehension, Knowledge, and Evaluation
Explanation:
- Prediction → Comprehension
- Listing events → Knowledge
- Writing a review → Evaluation
Bloom’s Taxonomy is an educational framework that classifies learning objectives into three domains—Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor. It helps teachers design structured learning experiences and assessments.
The revised Cognitive Domain (2001) includes six action-based levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. These levels support higher-order thinking and problem-solving.
Bloom’s Taxonomy faces criticism for its hierarchical structure, which some educators believe oversimplifies the learning process. Critics argue that lower-level skills are sometimes undervalued, even though they are essential for advanced learning.
Despite criticism, Bloom’s Taxonomy remains a powerful tool for designing curriculum, planning lessons, setting learning outcomes, and creating assessments. Its flexibility allows teachers to incorporate it into various teaching strategies.
CTET फरवरी 2026: परीक्षा अब 2 दिन होगी, CBSE का बड़ा फैसला
Challenges of Teaching Mathematics
Community Mathematics
Language of Mathematics
📘 Manipulatives for Effective Learning : Mathematics Pedagogy
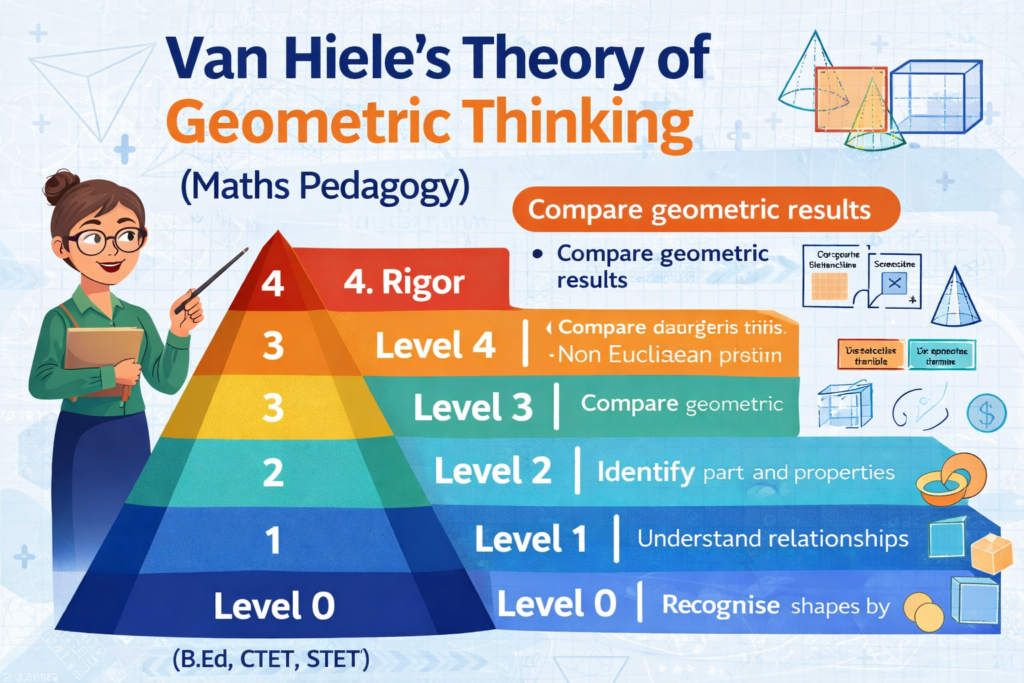
Van Hiele’s Theory of Geometric Thinking – Maths Pedagogy Notes
Introduction Understanding how students learn geometry is essential for effective mathematics teaching. Van Hiele’s Theory…