Diverse Classrooms: An Overview (विविध कक्षाएँ: एक परिचय)
A diverse classroom (विविध कक्षा) refers to an educational setting where students come from a variety of backgrounds (विभिन्न पृष्ठभूमियों से आते हैं), including differences in race (जाति), ethnicity (जातीयता), language (भाषा), socioeconomic status (सामाजिक-आर्थिक स्थिति), culture (संस्कृति), abilities (क्षमताएँ), and learning styles (अध्ययन शैलियाँ). In such environments, students bring unique perspectives (दृष्टिकोण), experiences (अनुभव), and needs (आवश्यकताएँ), which creates both challenges (चुनौतियाँ) and opportunities (अवसर) for teachers.

Key Features of a Diverse Classroom (विविध कक्षाओं की मुख्य विशेषताएँ):
- Cultural Diversity (सांस्कृतिक विविधता): Students may come from different racial, ethnic, or cultural backgrounds, influencing how they perceive the world and approach learning.
- Linguistic Diversity (भाषाई विविधता): Some students may speak different languages, which can affect their understanding (समझ) and communication (संचार) skills in the classroom.
- Learning Abilities and Styles (अध्ययन क्षमताएँ और शैलियाँ): Students have different learning abilities and preferences (पसंद). Some may excel in auditory learning (श्रव्य अध्ययन) while others may prefer visual or kinesthetic methods.
- Socioeconomic Differences (सामाजिक-आर्थिक भिन्नताएँ): Students may come from various economic backgrounds, influencing their access (प्रवेश) to resources (संसाधन) and opportunities outside of school.
- Inclusive Education (समावेशी शिक्षा): Diverse classrooms may include students with special needs (विशेष आवश्यकताएँ), requiring specific accommodations (विशिष्ट व्यवस्था) for full participation in learning.
Importance of Diverse Classrooms (विविध कक्षाओं का महत्त्व)
- Broadened Perspectives (विस्तारित दृष्टिकोण): Exposure to different cultures helps students develop a more well-rounded worldview (समग्र दृष्टिकोण), enabling them to appreciate (सराहना) diversity and understand other cultures.
- Preparation for the Real World (वास्तविक दुनिया के लिए तैयारी): In the real world, individuals interact with diverse groups in the workplace and society. A diverse classroom helps students learn how to collaborate (सहयोग करना) and solve problems in a multicultural environment.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking (सुधरी हुई आलोचनात्मक सोच): Being exposed to multiple viewpoints challenges students to think critically (आलोचनात्मक रूप से सोचना), improving their understanding.
Challenges of Teaching in a Diverse Classroom (विविध कक्षाओं में शिक्षण की चुनौतियाँ)
- Language Barriers (भाषाई बाधाएँ): Teachers may face difficulties when students are non-native speakers (मूल भाषा नहीं बोलने वाले) of the classroom’s language, requiring strategies to bridge communication gaps (संचार की खाई को पाटने के लिए रणनीतियाँ).
- Cultural Sensitivity (सांस्कृतिक संवेदनशीलता): Teachers need to be sensitive to different cultural norms (संस्कृतिक मानदंड), beliefs (विश्वास), and values (मूल्य) to create an inclusive (समावेशी) environment.
- Varying Learning Styles (विभिन्न अध्ययन शैलियाँ): Not all students learn the same way. Catering to these varied learning styles (विविध अध्ययन शैलियों) requires flexibility in teaching approaches.
- Differentiated Instruction (विभेदित निर्देश): Teachers need to adapt (अनुकूल बनाना) lessons to meet the diverse needs of students by using different teaching methods (अलग-अलग शिक्षण विधियाँ).
Strategies for Teaching in Diverse Classrooms (विविध कक्षाओं में शिक्षण के लिए रणनीतियाँ)
- Culturally Responsive Teaching (संस्कृति-संवेदनशील शिक्षण): Recognizing (पहचानना) students’ cultural backgrounds and integrating them into lessons is key to making learning more relevant for all students.
- Flexible Teaching Methods (लचीली शिक्षण विधियाँ): Use various teaching strategies (शिक्षण रणनीतियाँ) like group work, visual aids, technology, and hands-on activities to cater to different learning preferences.
- Inclusive Curriculum (समावेशी पाठ्यक्रम): Develop lesson plans that reflect the diversity (विविधता) of the student body, using examples from various cultures and perspectives.
- Classroom Environment (कक्षा का वातावरण): Create a respectful (सम्मानजनक) and welcoming classroom atmosphere where all students feel valued.
- Differentiated Learning (विभेदित अध्ययन): Tailor teaching to meet individual student needs by offering extra support (अतिरिक्त सहायता) to those who need it or providing advanced materials for fast learners.
Benefits of Diverse Classrooms (विविध कक्षाओं के लाभ)
- Enhanced Social Skills (सुधरे हुए सामाजिक कौशल): Diverse classrooms help students develop better communication (संचार) and social skills (सामाजिक कौशल) by interacting with peers from different backgrounds.
- Innovation and Creativity (नवाचार और सृजनात्मकता): Exposure to different perspectives encourages creative thinking (सृजनात्मक सोच) and innovative problem-solving (नवीन समाधान).
- Increased Empathy (बढ़ी हुई सहानुभूति): Understanding the experiences of others helps students develop empathy (सहानुभूति) and compassion (दया).
- Equity and Inclusion (समानता और समावेश): Diverse classrooms promote fairness (न्याय) and equal opportunities for all students, ensuring that no one is left behind.
Conclusion (निष्कर्ष)
A diverse classroom enriches the learning experience for both students and teachers. While it poses challenges, these can be turned into opportunities for growth (विकास), understanding (समझ), and collaboration (सहयोग). Teachers must foster an inclusive (समावेशी) and supportive (सहायक) environment where every student’s unique background (अद्वितीय पृष्ठभूमि) and perspectives are valued (मूल्यवान).
Challenges of Teaching & Learning Styles in a Diverse Classroom
Understanding who the students are, both as a group and as individuals, is an essential aspect of effective teaching. In a diverse classroom, the variety of students is much broader, and their needs can vary significantly. To facilitate the learning process for students from various backgrounds, the following points should be kept in mind:
- Treat all students as individuals, recognizing their unique strengths (ताकतें), weaknesses (कमज़ोरियाँ), and needs (ज़रूरतें), rather than generalizing them based on their racial, ethnic, or cultural background.
- Use a variety of teaching styles (शिक्षण शैलियाँ) to cater to the needs of diverse learners.
- Create an open and inclusive classroom that respects and values the experiences and perspectives of all students.
Learning Styles in a Diverse Classroom
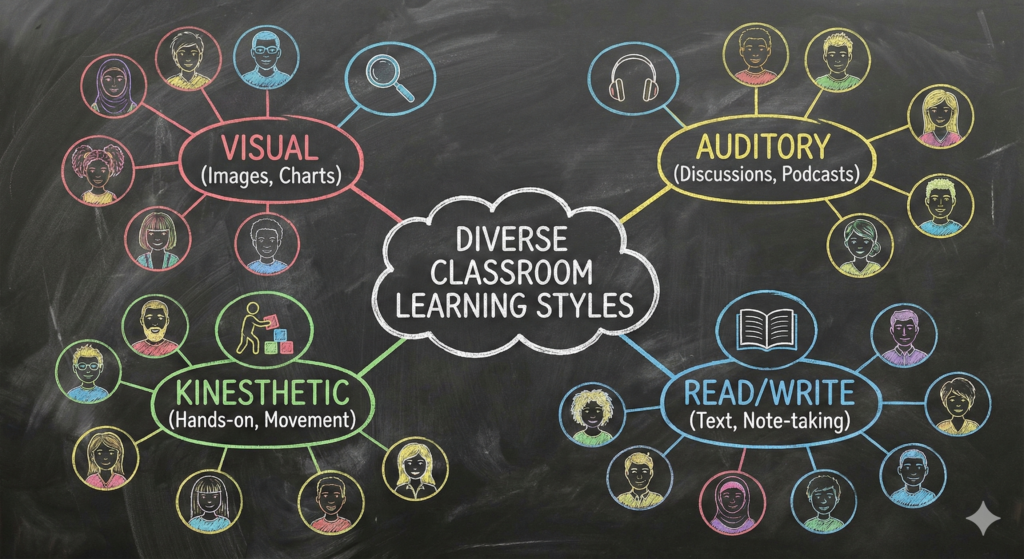
Eddy (1999) defines a learning style (अधिगम शैली) as the way individuals prefer to organize, classify, and assimilate information about their surroundings. According to Eddy, there are three primary learning styles:
1. Auditory Learners (श्रवण अधिगमकर्ता):
- Prefer receiving information by hearing (सुनना).
- These students may struggle with reading and writing but excel in memorizing spoken words (कथित शब्द) like song lyrics.
- They benefit from discussion-based (चर्चा-आधारित) classes and opportunities to give oral presentations (मौखिक प्रस्तुतियाँ).
2. Visual Learners (दृश्य अधिगमकर्ता):
- Prefer receiving information through visuals (दृश्य माध्यम), such as graphs and images.
- Pay close attention to details (विवरणों पर ध्यान).
- They may speak less in class and generally use fewer words when they do.
- Outlines (रूपरेखा), graphs (आरेख), and pictures (चित्र) are useful tools for their learning.
3. Kinesthetic-Tactile Learners (स्पर्श-गतिशील अधिगमकर्ता):
- Learn best through movement (गतिशीलता) and touch (स्पर्श).
- Often labeled as hyperactive (अति सक्रिय) due to their tendency to move around frequently.
- They enjoy movement-based learning, such as taking notes or learning through hands-on exploration.
NOTE: There is a fourth type too i.e. The Read/Writ Learner : As the name suggests, these individuals learn best through the written word. While visual learners need pictures and auditory learners need sound, Read/Write learners connect with text.
They absorb information most effectively by reading textbooks, handouts, and definitions. To truly grasp new concepts, they rely heavily on the physical act of writing. You will often find them taking detailed notes, making lists, or summarizing what they’ve read to lock the information into their memory.
Learning Environment for Children with Learning Difficulties (अधिगम कठिनाइयों वाले बच्चों के लिए अधिगम वातावरण)
Understanding different learning styles helps create more inclusive classrooms (समावेशी कक्षा) where everyone has the opportunity to succeed. However, some students face unique challenges, making learning in a traditional classroom setting difficult. These challenges may include:
- Visual impairments (दृष्टिबाधा)
- Hearing impairments (श्रवण बाधा)
- Attention Deficit Disorder (ध्यान कमी विकार)
- Mobility challenges (गतिशीलता की चुनौतियाँ)
- Learning disabilities (अधिगम अक्षमता)
Understanding Different Impairments and Disorders (अलग-अलग बाधाओं और विकारों को समझना)
- Visual Impairments (दृष्टिबाधा): Visual impairments refer to a condition where a person’s vision is either partially or completely limited (दृष्टि आंशिक या पूरी तरह से सीमित होती है). Students with visual impairments may face challenges in seeing the board, reading books, or navigating around the classroom.
Examples:- Blindness (अंधापन): Students with total blindness rely on braille (ब्रेल) or audio materials to read.
- Low Vision (कम दृष्टि): Students with low vision may use magnifying tools (आवर्धक उपकरण) or large-print materials to help them read and write.
- Hearing Impairments (श्रवण बाधा): Hearing impairments range from mild hearing loss to complete deafness (पूर्ण बहरापन). Students with hearing impairments might struggle with understanding spoken language (बोली गई भाषा को समझने में कठिनाई), especially in a noisy environment.
Examples:- Deafness (बहरापन): Students with profound deafness may use sign language (संकेत भाषा) as their primary means of communication.
- Hearing Loss (श्रवण हानि): Students with partial hearing loss may use hearing aids (श्रवण यंत्र) or lip-reading (होठों को पढ़ने) to follow conversations.
- Attention Deficit Disorder (ध्यान कमी विकार): Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are conditions where students struggle to maintain focus (ध्यान केंद्रित करने में कठिनाई होती है), are easily distracted (जल्दी विचलित होते हैं), or are hyperactive (अतिसक्रिय होते हैं). These students may have difficulty following instructions or staying on task for long periods.
Examples:- Inattention (अवधान): A student may frequently daydream (दिन में सपने देखना), miss important details, or have trouble organizing their work.
- Hyperactivity (अतिसक्रियता): A student might fidget (बिना रुके हिलना-डुलना), have difficulty sitting still, and may act impulsively (आवेग में कार्य करना) without thinking through consequences.
- Mobility Challenges (गतिशीलता की चुनौतियाँ): Students with mobility challenges have physical disabilities (शारीरिक अक्षमता) that limit their movement. These can be temporary, such as a broken leg, or long-term, like cerebral palsy (मस्तिष्क पक्षाघात) or spinal injuries.
Examples:- Wheelchair Users (व्हीलचेयर का उपयोग करने वाले): A student using a wheelchair may require ramps (रैंप) or wider spaces to navigate through the classroom.
- Difficulty Walking (चलने में कठिनाई): Some students may need crutches (बैसाखियाँ) or other mobility aids to move around the school.
- Learning Disabilities (अधिगम अक्षमता): Learning disabilities refer to conditions that affect how a person processes (प्रसंस्करण) and retains information (जानकारी रखना). These students may have average or above-average intelligence but still struggle with specific areas of learning.
Examples:- Dyslexia (वर्ण विकार): A student with dyslexia may find it challenging to read or recognize words (शब्दों को पढ़ने या पहचानने में कठिनाई), despite having normal intelligence.
- Dysgraphia (लेखन विकार): This refers to difficulty with writing (लेखन में कठिनाई), where students may have poor handwriting or trouble organizing thoughts on paper.
- Dyscalculia (गणितीय अक्षमता): This is a learning disability affecting the ability to understand numbers (संख्याओं को समझने में कठिनाई) and perform mathematical operations.
- Aphasia (अपाशिया): Aphasia is a communication disorder that affects a person’s ability to understand or produce language (भाषा को समझने या बनाने में कठिनाई). Students with aphasia may struggle with speaking, writing, or comprehending language, making classroom communication challenging. For example, a student may have difficulty expressing their thoughts clearly or following along with reading assignments.
- Auditory Processing Disorder (श्रवण प्रसंस्करण विकार): This condition affects how the brain processes auditory information (श्रवण जानकारी को संसाधित करने में कठिनाई). Students with auditory processing disorder may hear sounds but struggle to understand or interpret them, especially in noisy environments. For example, a student may find it difficult to follow multi-step verbal instructions, even if they can hear the words clearly.
Creating an Inclusive Classroom (समावेशी कक्षा का निर्माण)
Teachers can make their classrooms more inclusive by:
- Providing materials in accessible formats like braille, large print, or audio.
- Using visual aids and clear, concise instructions for students with hearing impairments.
- Allowing movement breaks or flexible seating for students with attention deficit disorders or mobility challenges.
- Offering personalized support or extra time for students with learning disabilities to help them grasp complex concepts.
By understanding the diverse needs of students, teachers can create a supportive learning environment that encourages success for all learners, regardless of their challenges (बाधाओं की परवाह किए बिना सफल होने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करता है).
Suggestions for Teachers Working with Students with functional Needs (विशेष आवश्यकताओं वाले विद्यार्थियों के साथ कार्य करने हेतु सुझाव):
- Treat each student as an individual (व्यक्ति), even if they have the same disability.
- Recognize that disabilities may not always be visible. Teachers should rely on authorized documentation (दस्तावेज़) rather than assessing a student’s health on their own.
- Use various modes of presentation (प्रस्तुति के विभिन्न तरीके) like written, verbal, video, or slides to help students with functional needs learn more effectively.
Tips on Teaching in a Diverse Classroom (विविध कक्षा में शिक्षण के लिए सुझाव)
- Appreciate the individuality (व्यक्तित्व) of each student. While generalizations may highlight key differences between groups, each student has unique values, perspectives, experiences, and needs.
- Clearly express early in the course that you are committed to meeting the needs of all students and are open to discussions on how to assist them in learning.
- Teachers must recognize their own learning styles (शिक्षण शैली) and cultural assumptions (सांस्कृतिक मान्यताएँ), as these can influence their teaching methods and expectations from students.
- Prepare multiple examples that reflect different cultures, genders, and experiences to ensure inclusivity in teaching.
- Help students bridge the gap between abstract knowledge (सैद्धांतिक ज्ञान) and concrete experiences (व्यावहारिक अनुभव).
- Use varied teaching methods (शिक्षण विधियाँ) such as lectures, group discussions, and collaborative learning to meet the diverse needs of students.
By incorporating different learning styles and understanding the challenges of teaching in a diverse classroom, teachers can create an environment where all students, regardless of their backgrounds or needs, have the chance to learn effectively and succeed.


Pingback: Pedagogy of English Language – (CTET English Pedagogy)