Learning & Acquisition
Language Acquisition vs Language Learning:
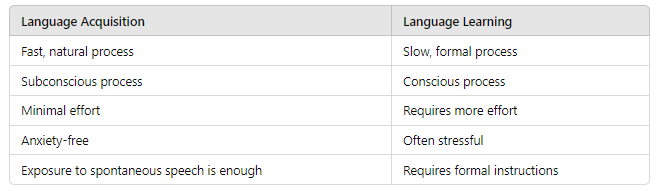
- Language Acquisition is a natural process through which learners understand and use a language by exposure, without formal instruction.
- Language Learning is a more formal process where learners study the language in a structured environment, often in a classroom setting.
Theories of Language Acquisition:
Cognitive Theory:
- Learning is a process where new information is connected to what we already know.
- It involves selecting the right grammar rules, and vocabulary, and using language appropriately in different situations.
- With practice, learners can improve their understanding and usage of language.
Discourse Theory:
- Emphasizes learning language through communication and social interaction.
- It focuses on how language learners discover meaning in real-life conversations.
- Children should be encouraged to engage in activities that promote communication to help them acquire language naturally.
Chomsky’s Universal Grammar Theory:
- Chomsky believes humans are born with an innate ability to learn language, which he calls Universal Grammar.
- Universal Grammar provides a set of rules that apply to all languages, making it possible for children to learn any language.
- He also introduced the concept of the Language Acquisition Device (LAD), which helps children automatically understand language structure from their environment.
Acquisition Strategies:
- Inductive Method: Learners first see examples and then try to figure out the rules.
- Deductive Method: Learners are taught the rules first, and then they apply them to examples.
Learning:
Definition of Learning:
- Richard E. Mayer: Learning is a long-term change in a person’s knowledge or behavior due to experience.
- Susan Ambrose: Learning is a process that leads to change, which enhances future performance and learning potential.
Types of Learning:
- Motor Learning: Learning physical activities like walking, driving, etc.
- Verbal Learning: Involves language, and communication using symbols, sounds, and words.
- Conceptual Learning: Involves higher mental processes like reasoning and understanding concepts.
Stages of Learning:
- Acquisition: Learning a new skill or task.
- Fluency/Proficiency: Improving accuracy in the new skill.
- Maintenance: Performing the task independently without further teaching.
- Generalisation: Applying the learned skill in different environments.
- Adaptation: Using the learned skill in new situations without guidance.
Aspects of Learning:
- Cognitive Aspect: Focuses on intellectual skills and knowledge.
- Affective Aspect: Involves emotions, attitudes, and values.
- Psychomotor Aspect: Focuses on physical skills and coordination.
Theories Related to Learning:
Piaget’s Concept:
- Learning happens through adaptation, which includes assimilation (integrating new information) and accommodation (adjusting thinking based on new information).
Vygotsky’s Concept:
- Learning occurs through social interactions. Knowledge is built through communication with more experienced individuals.
Pavlov’s Classical Conditioning:
- Learning through association. Pavlov demonstrated this with dogs, showing how they can learn to associate a bell with food.
Skinner’s Operant Conditioning:
- Learning through rewards and reinforcement. Positive and negative consequences influence behavior.
Inductive and Deductive Learning Methods:
- Inductive Method: Learners discover the rules by observing examples.
- Deductive Method: Learners are given the rules first, and then they apply them to examples.
Key Differences Between Language Acquisition and Language Learning:
English to Hindi Meaning of Tough Words:
- Acquisition – अर्जन
- Assimilation – आत्मसात करना
- Accommodation – समायोजन
- Discourse – संवाद
- Innate – जन्मजात
- Proficiency – निपुणता
- Generalisation – सामान्यीकरण
- Adaptation – अनुकूलन
- Reinforcement – प्रोत्साहन
Language and Acquisition: Important Links
Noam Chomsky & Innate Language Ability
https://www.britannica.com/biography/Noam-Chomsky
🔹 Difference Between Acquisition and Learning (British Council)
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/acquisition-vs-learning







Pingback: Pedagogy of English Language – (CTET English Pedagogy)