📢 इस लेख को हिंदी में कैसे पढ़ें?
मोबाइल पर:
- Google Chrome खोलें
- ऊपर दाईं ओर ⋮ (तीन डॉट) दबाएँ
- Translate पर टैप करें
- Hindi चुनें
Introduction
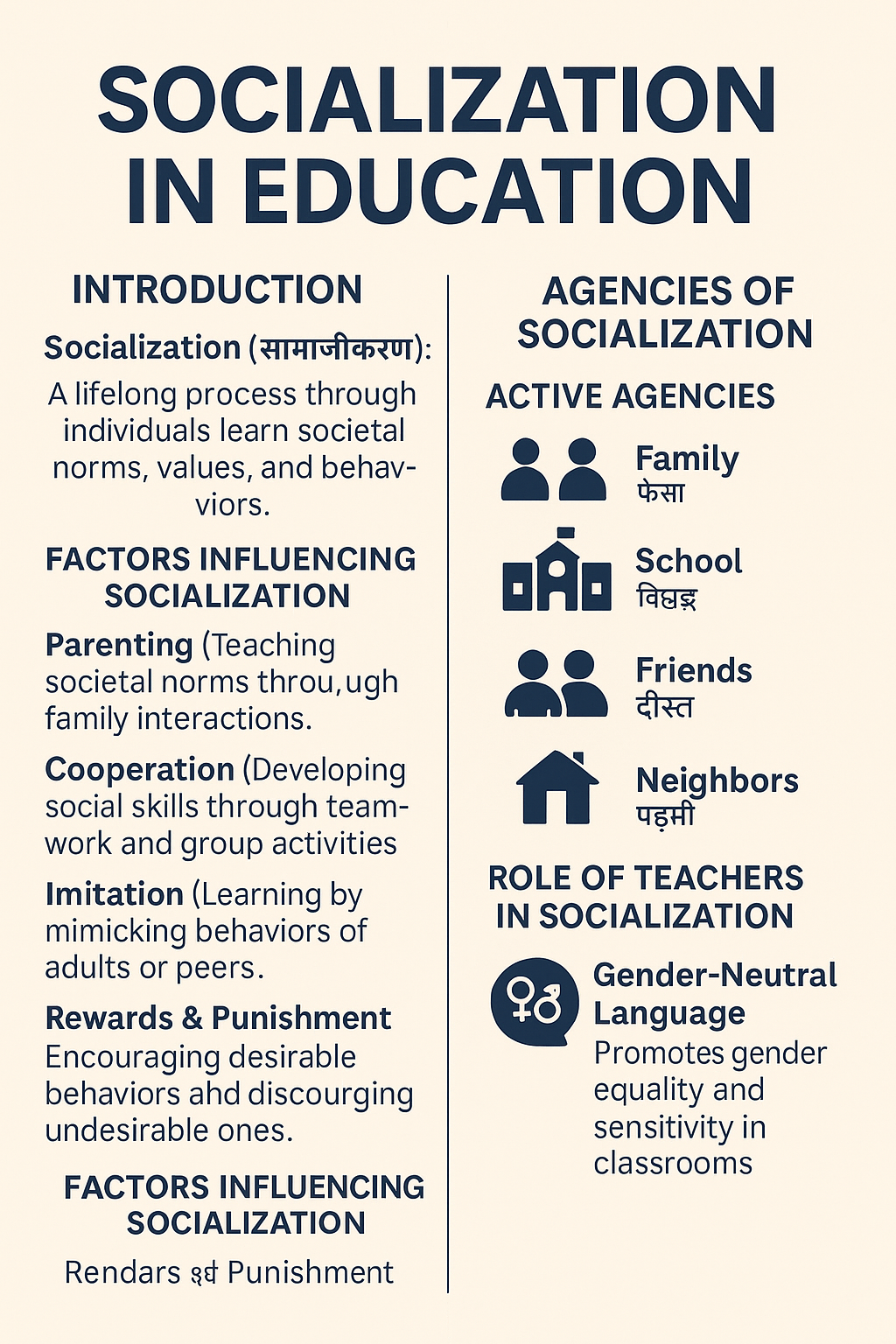
Socialization in Education- Socialization (सामाजीकरण) is a lifelong process in which individuals learn the norms, values, and behaviors of society. It starts at birth and continues throughout life. Through this process, children gradually understand how to act, communicate, and participate in their cultural environment.
Factors Influencing Socialization
Parenting (पालन-पोषण)
Parents teach values, manners, and daily habits through direct interaction. Children learn society’s expectations mainly from family.
Cooperation (सहयोग)
Children develop teamwork and social skills when they work with others during games, tasks, and group activities.
Imitation (अनुकरण)
Young learners often copy the behavior of adults, teachers, and peers. They adopt language, gestures, and habits through imitation.
Rewards and Punishment (पुरस्कार एवं दण्ड)
Rewards encourage desirable behavior, while consequences help children understand which actions society discourages.
Agencies of Socialization
1. Active Agencies (सक्रिय एजेंसियाँ)
Active agencies directly involve children in social experiences. They influence behavior immediately because children participate in them every day.
Examples:
• Family (परिवार)
• School (विद्यालय)
• Friends (दोस्त)
• Neighbors (पड़ोसी)
2. Passive Agencies (निष्क्रिय एजेंसियाँ)
Passive agencies influence children indirectly. Children observe these institutions or interact with them occasionally, yet they still shape their understanding of society.
Examples:
• Police Station (पुलिस स्टेशन)
• Public Library (सार्वजनिक पुस्तकालय)
• Railway Station (रेलवे स्टेशन)
Role of Teachers in Socialization
Use of Gender-Neutral Language
Teachers promote equality by using gender-neutral words such as:
• Cameraperson instead of Cameraman
• Chairperson instead of Chairman
This practice encourages fairness, respect, and sensitivity among students. Teachers also guide children toward positive behavior, cooperation, discipline, and empathy through daily interactions.
Examples in Education
Active Agency in Schools
Group discussions, role-plays, and team projects help children learn cooperation, communication, and problem-solving.
Passive Agency in Media
Children learn about society’s diversity from books, cartoons, newspapers, and educational programs. They absorb attitudes, ideas, and cultural patterns through observation.
Key Takeaways
• Socialization helps children become active and responsible members of society.
• Child-centered education naturally supports socialization through play, activities, and collaborative learning.
• Gender-neutral language promotes social justice and equality in classrooms.
• Teachers play a crucial role in shaping values, identity, and social behavior.
Glossary
| Term | Hindi | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Socialization | सामाजीकरण | Learning norms, values, and behaviors of society. |
| Active Agency | सक्रिय एजेंसी | Institutions where children participate directly (family, school). |
| Passive Agency | निष्क्रिय एजेंसी | Institutions that influence indirectly (libraries, stations). |
| Imitation | अनुकरण | Learning by copying others. |
| Gender-Neutral Language | लैंगिक समावेशी भाषा | Language that avoids gender-specific terms. |
Core Concept
Socialization prepares individuals to adapt to their culture and develop their identity, values, and role in society.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR CTET BASED ON SOCIALISATION
1. A teacher replaces words like “Chairman” with “Chairperson” during class discussions. This promotes—
A. Language accuracy
B. Gender-neutral language
C. Punishment-based learning
D. Formal classroom tone
2. A student learns table manners by observing parents at the dining table. This is an example of—
A. Cooperation
B. Imitation
C. Reward
D. Passive agency
3. A child learns how to behave in a queue by observing people at a railway station. Which type of agency is involved?
A. Active agency
B. Passive agency
C. School agency
D. Peer agency
4. A teacher forms mixed-gender groups and encourages equal participation. This supports—
A. Competition
B. Individual learning
C. Social justice and inclusivity
D. Memory-based learning
5. Children develop leadership and teamwork through group projects. This is an example of socialization through—
A. Punishment
B. Cooperation
C. Imitation
D. Observation
6. A school organizes activities like role-plays, storytelling, and group games. These help in—
A. Rote memorization
B. Child-centered socialization
C. Strict discipline
D. Uniform behavior
7. A child copies the way a teacher greets students every morning. This is—
A. Reward
B. Imitation
C. Passive socialization
D. Cooperation
8. Police stations and courts influence a child’s understanding of societal systems even without direct instruction. These are—
A. Active agencies
B. Passive agencies
C. Formal agencies
D. Peer groups
9. A teacher appreciates students who help classmates during activities. This supports—
A. Individual competition
B. Encouragement of desirable behavior
C. Punishment
D. Gender stereotyping
10. A child learns honesty because parents consistently model honest behavior. This is socialization through—
A. Reward
B. Imitation and family agency
C. Punishment
D. Books only
11. A teacher encourages students to speak in class without fear. This contributes to—
A. Rote learning
B. Social confidence and participation
C. Punitive discipline
D. Gender bias
12. A child enjoys reading because the home has many books and family members read regularly. This reflects the influence of—
A. Punishment
B. Media agency
C. Family as an active agency
D. Peer pressure
13. Students learn values like fairness and cooperation by playing team sports in school. This is an example of—
A. Negative reinforcement
B. Passive agency
C. Active socialization in school
D. Monotonous learning
14. A teacher uses inclusive language like “students” instead of “boys and girls.” This helps reduce—
A. Academic load
B. Homework pressure
C. Gender stereotyping
D. Peer conflict
15. A child observes diversity in clothing, food, and behavior while watching TV shows. This is socialization through—
A. Family
B. Friends
C. Media as passive agency
D. Reward method
- CTET फरवरी 2026: परीक्षा अब 2 दिन होगी, CBSE का बड़ा फैसला

- Challenges of Teaching Mathematics

- Community Mathematics

- Language of Mathematics

- 📘 Manipulatives for Effective Learning : Mathematics Pedagogy

Internal & External Links
CTET फरवरी 2026: परीक्षा अब 2 दिन होगी, CBSE का बड़ा फैसला
Challenges of Teaching Mathematics
Community Mathematics
Language of Mathematics
📘 Manipulatives for Effective Learning : Mathematics Pedagogy
Van Hiele’s Theory of Geometric Thinking – Maths Pedagogy Notes
Introduction Understanding how students learn geometry is essential for effective mathematics teaching. Van Hiele’s Theory…